Discover how to calculate and manage your burn rate to ensure your startup’s financial stability and long-term success. Learn why it’s crucial for growth.
Table of Contents
What’s Burn Rate?
Burn Rate is a critical financial metric that measures the rate at which a startup is spending its capital before reaching profitability. It represents the amount of cash a company is losing on a monthly basis. There are two types of burn rates:
- Gross Burn Rate refers to the total amount of operating expenses incurred each month.
- Net Burn Rate accounts for the revenue generated, showing how much cash is being lost after subtracting revenues from expenses.
Understanding your burn rate is essential for managing cash flow and planning future funding needs. It helps you gauge how long you can sustain operations before requiring additional capital or achieving profitability.
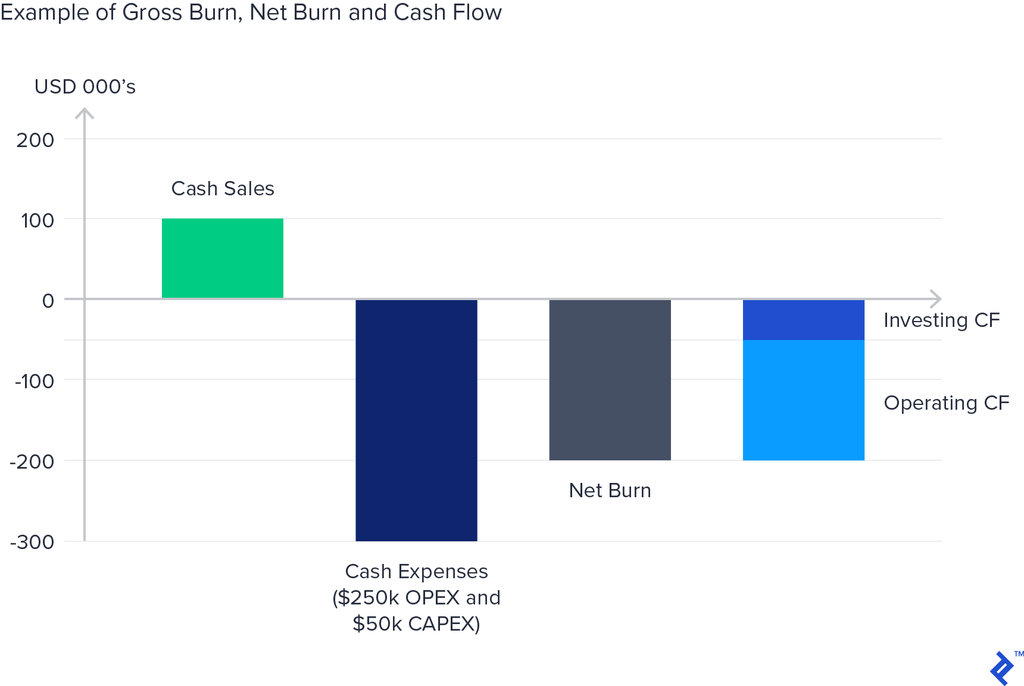
Why Burn Rate Matters
Burn Rate is crucial for startups because it provides insight into the sustainability of your business model and financial health. A high burn rate can signal that you are spending too quickly relative to your revenue, potentially leading to cash shortages. Conversely, a low burn rate indicates effective expense management and a longer runway before needing additional funding.
Monitoring your burn rate helps you make informed decisions about scaling operations, seeking investment, and adjusting your budget to ensure the long-term viability of your startup.
How to Use Burn Rate for Your Startup
- Calculate Your Burn Rate: Determine your Gross Burn Rate and Net Burn Rate by analyzing your monthly operating expenses and revenue. This provides a clear picture of how much cash you are consuming.
- Project Your Runway: Use your burn rate to calculate your financial runway, which is the amount of time you have before running out of cash. This is crucial for planning future funding rounds or cost-cutting measures.
- Optimize Spending: Regularly review your expenses and identify areas where you can reduce costs without compromising growth potential. Aim to improve your burn rate by increasing efficiency and maximizing revenue.
- Plan for Funding: Understanding your burn rate helps you determine when to seek additional investment and how much funding you might need to reach your next milestones.
Formula for Calculating Burn Rate
The formula for calculating Burn Rate is:
Burn Rate = Total Monthly Expenses – Monthly Revenue
Example: If your startup has total monthly expenses of $50,000 and generates $10,000 in monthly revenue, your Net Burn Rate would be:
Burn Rate = $50,000 – $10,000 = $40,000
This means you are burning $40,000 in cash each month.
Example of Burn Rate in Action
Imagine you run a tech startup with a monthly gross burn rate of $80,000 and monthly revenue of $20,000. Your net burn rate is $60,000, indicating you are spending $60,000 more than you are earning each month. With $600,000 in your bank account, your runway would be 10 months, giving you time to adjust strategies or seek additional funding before your cash runs out.
FAQ
Why is the burn rate important for startups?
Burn rate helps startups understand how quickly they are using their capital and how long they can sustain operations before needing additional funding or reaching profitability. It’s vital for managing cash flow and financial planning.
How can I improve my startup’s burn rate?
To improve your burn rate, focus on reducing unnecessary expenses, optimizing operations for efficiency, and increasing revenue. Regularly review and adjust your budget based on your financial performance.
What should I do if my burn rate is too high?
If your burn rate is too high, consider cutting non-essential costs, finding ways to increase revenue, or seeking additional investment to extend your runway. Reevaluate your business model and financial strategies to ensure sustainability.
To understand more about startup KPIs, please see the Startup KPIs articles.
For more information about KPIs and prioritization for an early-stage startup, we recommend this video from Y Combinator Startup School.

Leave a Reply